There are polymers like ABS, PA (Nylon), or PC that can be both CNC machined and 3D printed, so it is a common question when to use polymer CNC machining and when to use 3D printing. This article will walk you through the main differences between machining and printing polymers and suggests several questions you need to ask yourself to choose the right option.
Two approaches: subtractive and additive manufacturing
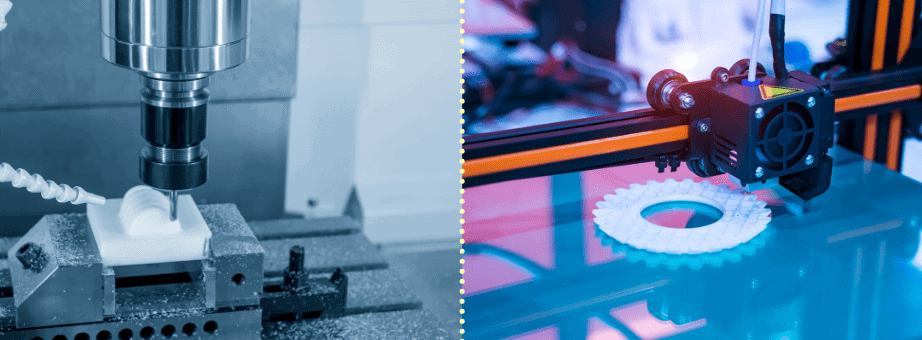
While the end results might be similar, CNC machining and 3D printing operate in ways opposite to each other.
CNC machining (subtractive process)
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that begins with a solid block of plastic material, cut or shaped into the desired product by excess material using a variety of sharp rotating tools or cutters.

3D printing (additive process)
3D printing is additive manufacturing, which means the initial material is built layer by layer, rather than removed as in subtractive manufacturing. 3D printing creates three-dimensional objects from reading a virtual computer design and reproduces it into a real and intangible part by using material filaments or powders.

Checklist to choose between CNC machining and 3D printing
When it comes to the selection of either CNC machining or 3D printing to produce polymer parts, we recommend you to answer a few basic questions.